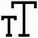NOMATEN HYBRID-SEMINAR, SEPTEMBER 26th, About the formation of vacancy clusters in fcc metals: an atomistic approach
In-person: NOMATEN seminar room
NOMATEN HYBRID-SEMINAR
online: https://www.gotomeet.me/NCBJmeetings/nomaten-seminar
In-person: NOMATEN seminar room
Tuesday, September 26th 2023 13:00 CET
About the formation of vacancy clusters in fcc metals: an atomistic approach.
Dr. Marie Landeiro Dos Reis
La Rochelle Université, France
Abstract:
Vacancy clusters have a major contribution in multiple mechanisms as oxidation, precipitation and creep and can lead to material premature cracking. It is thus essential to have a deep understanding of the stability of these defects under a wide range of stress and temperature. Multiple factors influence the formation of the clusters, yet the preponderant factor seems to be the presence of a gaseous environment, like H [1,2,3].
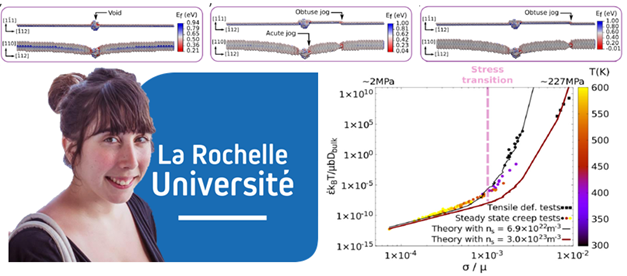
For this purpose, we investigate at the atomic-scale the formation of such clusters. Using empirical force fields derived from EAM potentials we show that the interaction between point-defects is very attractive which favor the formation of voids. We found that the absorption of point-defects by the clusters is slightly anisotropic. It occurs at the cluster poles in {100} directions for vacancies and {110} directions for H interstitial atoms. We determine their stable shape for various fcc metals: Al, Pd, Ni, Cu, Au, Ag. Finally, we show that H not only drastically decrease the formation energy and influence the stable shape of the defects but has also an influence in the long range elastic distortion. Hence that have a direct consequence on the interaction between the voids with dislocations and the other material defects and those impact the mechanical properties in term of elastic and plastic behavior [4,5].
[1] L. Clarebrough et al., Acta Metall. 15 (6) (1967)
[2] B. Eyre, J. Phys. F: Met. Phys. 3 (2) (1973)
[3] Y. Fukai (2006) The metal-hydrogen system: basic bulk properties
[4] G. Hachet et al., Acta Mater. 148 (2018) 280-288
[5] K. Arakawa, et al. ISIJ International, 61 (2021) 2305-2307
Bio:
Marie Landeiro pursued a PhD at SRMP CEA Saclay between 2016 and 2019, under the supervision of Laurent Proville, on the dislocation mobility in metals. Using numerical simulations, They developed a multi scale model to study the dislocation propagation in a distribution of vacancy-clusters over time, under stress and temperature. After her PhD Marie worked on the interaction between dislocation and vacancy in magnesium oxide, at Lille university in UMET laboratory under the supervision of Philippe Carrez and Patrick Cordier. In February 2021 she moved to Laboratoire des sciences de l'ingénieur pour l'environnement (LASIE) in La Rochelle to study interactions between hydrogen and vacancies in nickel. Since September 2021, Marie has held a position of Associate Professor (Maîtresse de Conférences) à La Rochelle Université.
Tags